 Our Universe is full of mysterious objects including planets, stars, galaxies, and dark matter. Humans have successfully conducted many space mission from more than a half-century. We have found a lot about our universe, galaxy, and the solar system. Among these space missions, we have chosen the top 10 most important space missions that have changed our perceptions in the field of astronomy and physics.
Our Universe is full of mysterious objects including planets, stars, galaxies, and dark matter. Humans have successfully conducted many space mission from more than a half-century. We have found a lot about our universe, galaxy, and the solar system. Among these space missions, we have chosen the top 10 most important space missions that have changed our perceptions in the field of astronomy and physics.
Apollo 11
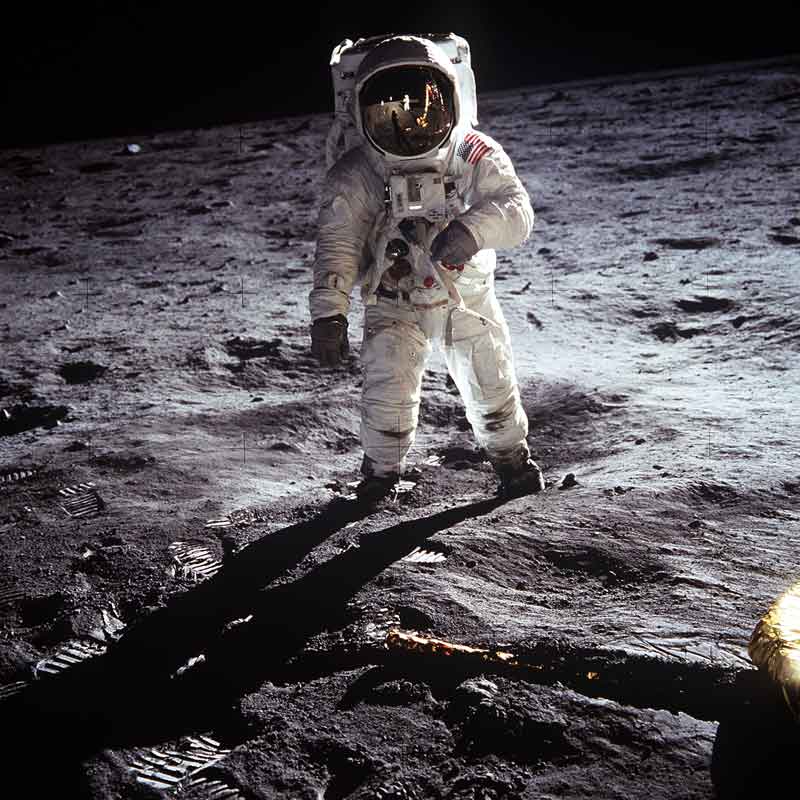

The greatest accomplished space mission in the history of humankind is the moon landing by Apollo 11. The mission was successfully launched on 16 July 1969 with the crew of three; Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Mike Collins.
The spacecraft was mainly divided into two parts; the command module and the lunar module. The command module was designed to stay in the orbit of the moon for communication and to take the astronauts back to the Earth. Whereas, the lunar module was designed to land on the moon with two crew members; Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin. The landing on the moon happened on the 20th of July and was witnessed by more than 500 million people on the Earth.
Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin performed many trips to different locations of the moon over the time period of 20 hours. They collected samples of rock and sand to bring it back to the Earth. They also performed several experiments, talked live with US President, and saluted the US flag that they fixed.
Curiosity
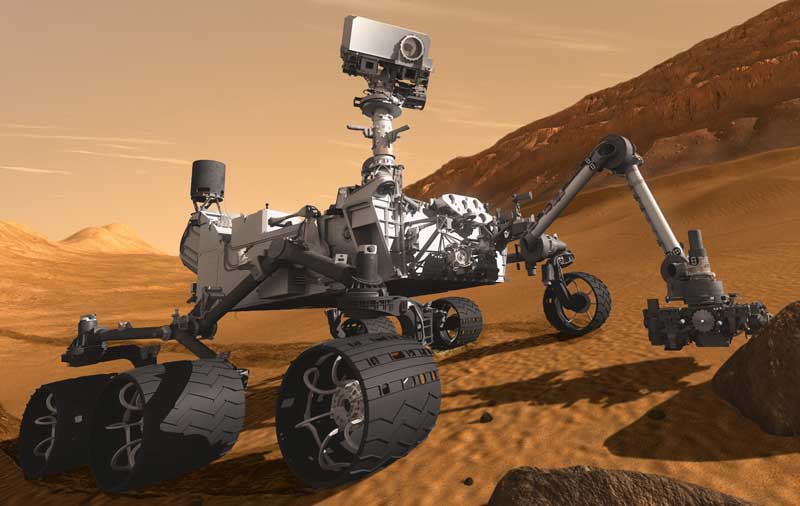

The most sophisticated rover designed with cutting-edge technology, curiosity, was launched on Atlas V rocket in 2011 towards Mars. This Martian rover was equipped with the most advanced and expensive scientific equipment to analyze the Martian Land.
Curiosity entered the atmosphere of Mars and landed successfully with the help of a parachute in August of 2012. The main goal of the curiosity on Mars was to search for the evidence about the past condition of Mars. Curiosity has found some evidence that in the past – about 4.2 billion years ago – Mars was more habitable, and there was the presence of liquid water.
International Space Station Missions – ISS
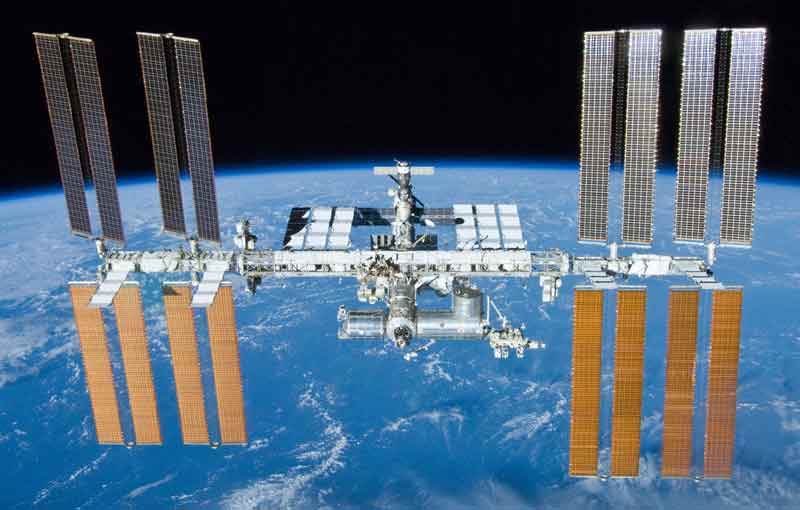

International Space Station was constructed by the joint missions from around the world. It is still developing with the help of many nations including the United States and Russia. The first module of the ISS was sent by Russians in the 1990s. After which several missions were sent to ISS to construct it further and the first crew went to ISS in 2000. Today, the ISS is orbiting around the Earth at a height 350 kilometers above the ground with a speed of 8 km/h.
The main purpose of the ISS is to provide the scientists with an experimental laboratory in zero gravity of space environment. The environment that scientists get on ISS for experiments in nearly impossible to achieve 100% on the Earth.
WMAP Satellite
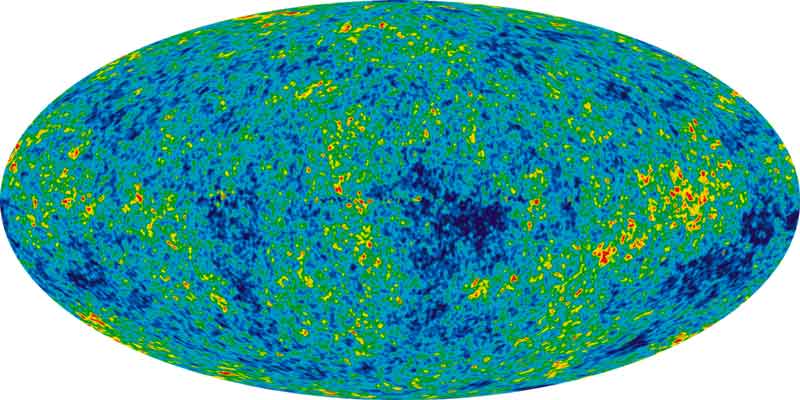
Our universe is the result of sudden of expansion caused by the big bang from something infinitesimally small. Scientists always wanted to know the conditions of the universe at that time. They have made predictions and now it was time to collect the evidence to confirm them. One way was to capture the photons emitted after 380,000 years of the big bang and see the conditions of the universe. These early photons are called cosmic microwave background radiations that fall on the Earth from every direction of the space.
Scientists needed a high-resolution image of these radiations to know more about the early universe. For this purpose, NASA developed a spacecraft called Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) to capture the photons and make a good quality image. The WMAP captured a good quality image which proved that the universe in early time was uniform in temperature and confirmed many predictions.
Viking I and Viking II
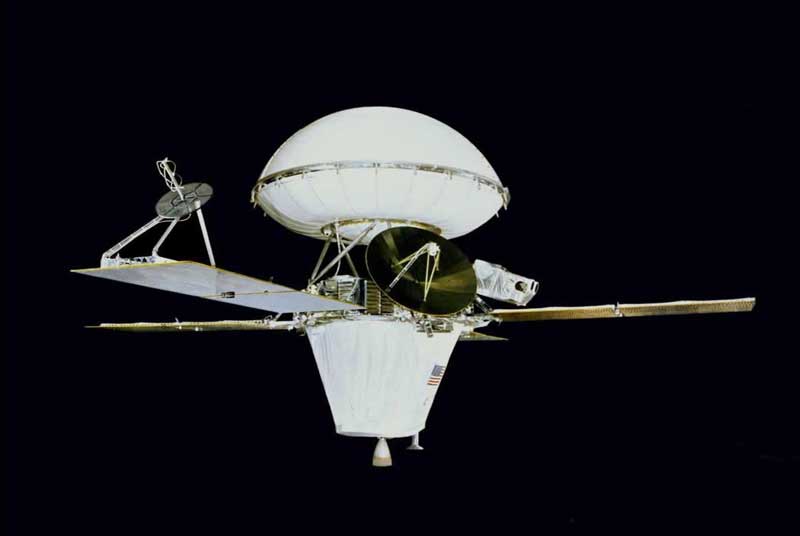

Landing on Mars was a very difficult task and there have been many failed missions to land on Mars. Viking probes were the first that successfully landed on the surface of Mars and studied it. Viking I and Viking II are the twin vehicles developed by NASA to study the red planet, Mars.
The two space probes were totally identical and consisted of two parts; an orbiter and a lander. The lander was designed to land on Mars to study its surface. Whereas, the purpose of the orbiter was to enter the orbit of Mars and take photographs. Also, the orbiter provided a communication medium between lander and stations on the Earth.
These two space probes were launched within the period of one month; Viking 1 was launched on 20 August 1975, and Viking II on 9th September 1975. Both of them were launched on the Titan IIIE rocket. The space probes provided evidence that life doesn’t exist on Mars.
Venera Space Probes

Venus is the 2nd planet from the Sun and is the hottest planet in the solar system with a temperature of 462 °C. The atmosphere of Venus is very thick which makes it difficult to study its surface with space telescopes. To study more about this hottest planet and its surface, the Soviet Space Program funded a series of space probes called Venera space probes to study Venus.
There were 23 space probes that were launched from 1961 to 1984. Out of 23 probes, 10 were designed to land on the surface of Venus. Due to the very hot atmosphere, the probes were only able to operate for 2 hours before the hot atmosphere destroyed them. In the period of 2 hours, these probes sent photographs of Venus’s surface along with other scientific data.
Vostok 1
There have been many spaceflights to space before 1961 but without humans ever crossing the outer space. Vostok 1 was spaceflight operated totally by the Soviet Union which became the first to send a human to cross outer space. The lucky man was Yuri Gagarin who in 1961 became the first man to experience the outer space.
Before the Vostok 1 spaceflight, scientists were not sure how the human body will feel the weightless environment in outer space. So, extra precautions were taken to make the spaceflight successful which are now unnecessary. It was one of the most important spaceflights which opened the gateway for humans to go in outer space for the first time.
STS-1 – Space Transportation System-1
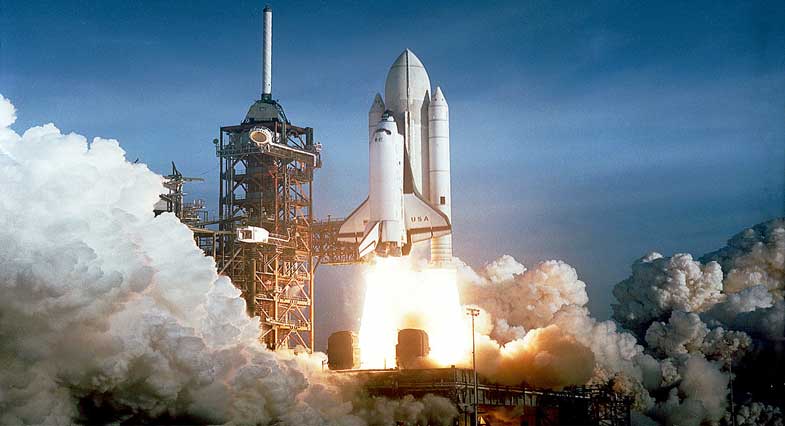

NASA launched many satellites and space probes in space successfully. The problem with the launches was the cost; it was too expensive to launch something in rockets. To tackle this issue, NASA started to develop a reusable rocket system to reduce the launch cost. NASA succeeded to develop a reusable rocket system called space shuttle. The first flight of space shuttle is called STS-1 and it was launched on 12th April 1981.
Space Shuttle is a reusable space vehicle whose main components are orbiter vehicles with three main engines, recoverable solid rocket booster, and an external tank that is filled with liquid hydrogen and oxygen fuel.
Voyager I and Voyager II
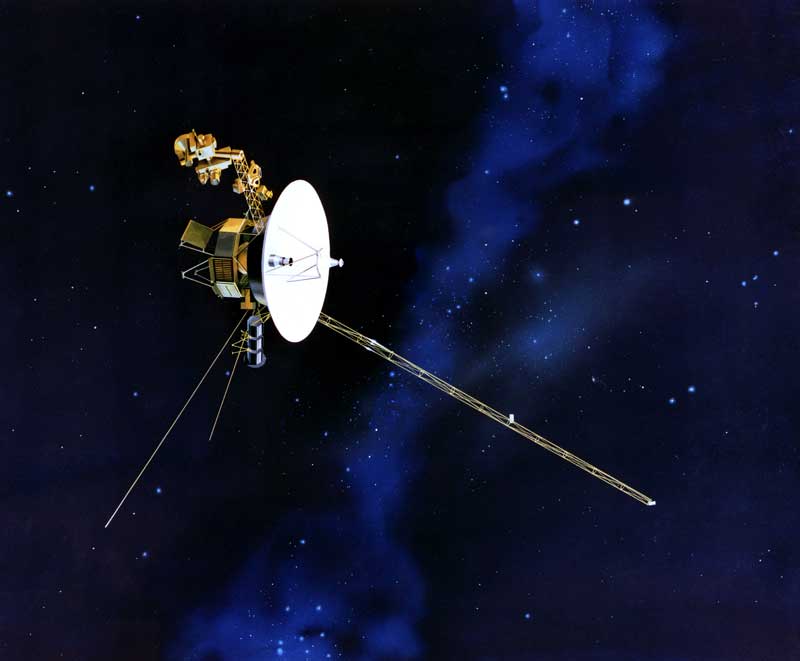

Voyager I and Voyager II are the two deep space exploration probes that were launched in late 1977. The main goal of these two probes was to study the four gas giants in the solar system which are Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus. They studied and captured the high-quality photos of four giants over the time period of 10 years. These space probes were designed to receive power from a radioactive element, Plutonium-238.
The space probes successfully completed their primary mission and were still operational. So, their mission was extended to the boundaries of our solar system and interstellar space. Today, these space probes are still operational and are sending data to Earth. Voyager I has gone very far into space and has achieved the title of the farthest man-made object in space. It has just crossed the boundaries of our solar system and is on the course to interstellar space.
New Horizons
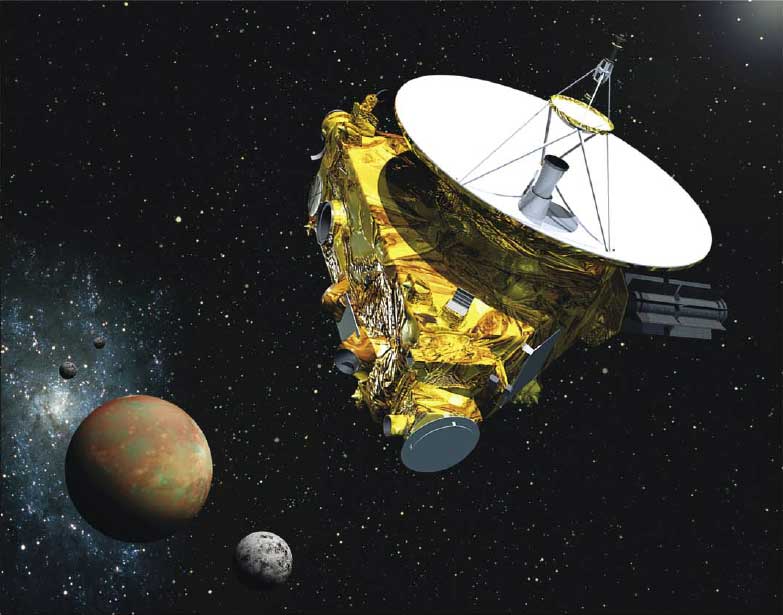

Pluto, the dwarf planet, was once considered a planet is very far from Earth that studying it with the telescope was very difficult. So, NASA developed a spacecraft, New Horizons, to study the Pluto closely and take its high-quality photographs. The spacecraft was launched from the Earth in 2006 and reached the Pluto in July of 2015 – took about 9 years. Before the New Horizons’ flyby near Pluto, we hadn’t any clear photograph of Pluto. It was the first time when New Horizons took very high-quality photographs and gathered other scientific data to study more about Pluto.
New Horizons was a very fast traveling spacecraft ever sent by NASA. When it left the orbit of the Earth successfully, it reached a speed of 60,000 km/h. It so far from the Earth that the signals traveling between the Earth and the spacecraft take about 3 hours.






